what command would you use to delete the tasks table from the bits database?
The correct application of the DELETE statement for data removal is crucial, and it involves lots of problems. Withal, there are standard practices of the DELETE statement usage that simplify all such tasks.
This article will explore some of the professional life scenarios to equip yous with the nearly helpful tips to use the DELETE statement correctly. You can remove data from a table in unlike ways. Explore the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE in SQL Server that has been covered with practical examples.
T-SQLDeleteControlBasics
First of all, we should go familiar with the T-SQL Delete statement in the simplest style possible.
The Delete statement, as the proper name indicates, is a statement that helps us to delete information from the database table.
A tabular array is a structure that yous create in a database to store your data. For case, nosotros tin take a table of books to store records related to those books.
A database is an organized collection of information and the data structures to concur that data. In other words, information can be stored inside the database in the form of tables.
How to Delete I Row or Multiple Rows
We can delete i or more records (commonly known equally rows) from a table using the delete statement.
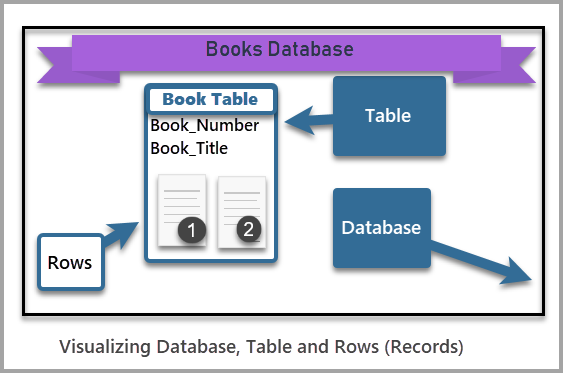
The Delete argument removes some or all data (rows) from a table.
According to Microsoft documentation, the Delete statement removes one or more rows from a table or view in SQL Server.
One might wonder how the statement defines whether to remove some or all of the data (rows) from a tabular array. The reply lies in the criteria or conditions specifying what needs to be removed.
Delete Command in SQL Server
The simplest syntax of the argument is as follows:
Delete FROM <TableName> WHERE <Condition> You need to provide the table name and the criteria/condition for the data (rows) deletion from the tabular array.
Notation: Information technology is crucial to use the DELETE statement with a condition (WHERE Clause) although the condition requirement is not a must.
If you lot execute the DELETE tabular array command without the WHERE status, you will end upward deleting all the rows (data) from the table. Hence, brand it a habit to use the WHERE status unless you want to remove all rows.
Compatibility
This statement is compatible with many versions of SQL Server, including the post-obit:
- SQL Server 2012 and up versions.
- Deject-based SQL Server Database (Azure SQL Database).
- Cloud-based SQL Data Warehouse (Azure Synapse Analytics).
Step-by-stride Checklist to Remove Rows from the Table
Now we are going to explore the Delete statement usage with several practical scenarios.
The Summary of Steps
- Setup a Sample Database.
- View the data.
- Delete the data.
- Insert more data back into the table.
- View the data earlier deletion.
- How to delete data in a column based on a condition.
- View the data later on deletion.
- Insert more data back into the table.
- View the data before deletion.
- Delete the data based on another condition.
- View the data after deletion.
- Insert the information back into the tabular array.
- Delete the data based on two weather condition this fourth dimension.
- View the data subsequently deletion.
Setup Sample Database (BooksSample)
We demand a sample database to test and run the scripts. Kickoff, nosotros need to set that sample database up, covering the post-obit steps:
- Create a sample database.
- Create a tabular array in the sample database.
- Insert the information (two rows) into the database tabular array.
Open SQL Server Management Studio or dbForge Studio for SQL Server and execute the following script to fix the sample database:
-- Connect to the 'master' database to run this snippet USE master GO -- Create a new database if it does not already exist IF NOT EXISTS ( SELECT [proper noun] FROM sys.databases WHERE [proper name] = N'BooksSample' ) CREATE DATABASE BooksSample Get USE BooksSample -- Create the tabular array book CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Book] ( [BookNumber] INT Not Zero PRIMARY Key,-- Primary Key column [Championship] VARCHAR(150) Not NULL, [Stock] SMALLINT Non NULL ); GO -- Insert rows into table 'Volume' INSERT INTO [dbo].[Book] ( -- Columns to insert data into [BookNumber], [Championship], [Stock] ) VALUES ( -- Outset row: values for the columns in the list above 1, 'Learn SQL in 7 Days', fifty ), ( -- Second row: values for the columns in the list above ii, 'Creating Databases in Minutes', l ); GO View the information (Book table)
Allow united states of america view the recently created and populated table in the database. Run the beneath script:
-- View data (rows) from the table (Book) SELECT b.BookNumber, b.Title, b.Stock FROM dbo.Book b The output is:
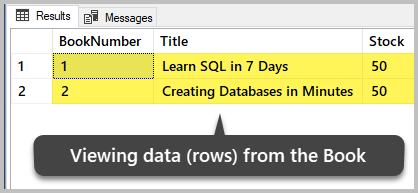
We tin can see the two rows of the table (Book). At the moment, these are all the data present in this tabular array.
Delete the Data
Every bit nosotros remember, there is a hazard of deleting all rows in a table if we forget to mention the condition/criteria for the correct deletion.
Ever use the WHERE Clause with the Delete statement to avert adventitious data loss. The only exception should be the case when you need to delete all data intentionally.
To remove all information (rows) from the sample database table, run the following script:
-- Delete all the data (rows) from the tabular array Volume DELETE FROM dbo.Book The output is:
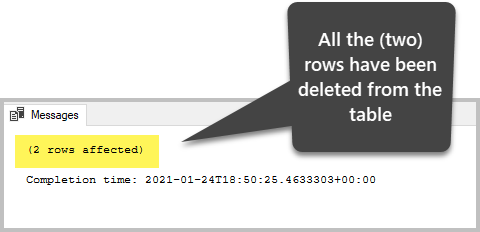
View the data subsequently the deletion
At present, we need to check if all the rows accept been deleted:
-- View data (rows) from the table (Book) SELECT b.BookNumber, b.Championship, b.Stock FROM dbo.Book b The results are:
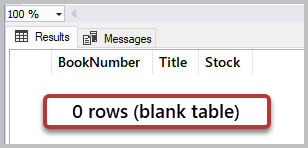
This way, we have successfully deleted all the rows from the Book tabular array. For that, we practical the DELETE argument without any deletion criteria/conditions.
Insert Information Back into the Table (with the Same Title)
Nosotros can insert the data (rows) back into the tabular array and then apply the DELETE statement based on some atmospheric condition/criteria.
This time, we cull to insert more rows, simply deliberately having the same title:
-- Insert rows into table 'Book' INSERT INTO [dbo].[Volume] ( -- Columns to insert information into [BookNumber], [Title], [Stock] ) VALUES ( -- Get-go row: values for the columns in the list in a higher place one, 'Learn SQL in 7 Days', l ), ( -- 2nd row: values for the columns in the listing above 2, 'Creating Databases in Minutes', l ), ( -- Third row: values for the columns in the list above 3, 'Creating Databases in Minutes', 50 ), ( -- Fourth row: values for the columns in the list above iv, 'Creating Databases in Minutes', l ); Go The output is as follows:
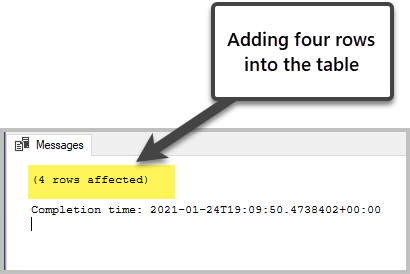
Note: To restore the deleted or changed information, you can use the dedicated software solutions. The dbForge Transaction Log solution allows you both to restore those data and view who and when deleted or altered them.
View the data before deletion
To view the data, execute the post-obit script:
-- View data (rows) from the table (Book) SELECT b.BookNumber, b.Championship, b.Stock FROM dbo.Volume b The output is:
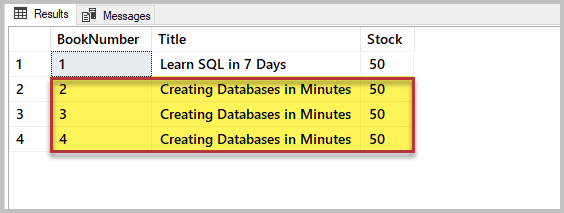
The output demonstrates that we take inserted three rows with the same book title by mistake. It is a problem. The uncomplicated solution is to remove the unnecessary rows, applying the specific status for removing rows with duplicate titles.
How to Delete Information in SQL Cavalcade Based on a Status (BookNumber)
Important: Nosotros may consider one of the following means to solve this trouble:
- Delete by BookNumber
- Delete by Title
In my scenario, I cull not to delete past Championship. If we delete past Title, we end up deleting all rows containing that championship including those nosotros need to go along. Hence, the recommended approach is to remove the table based on the BookNumber column.
If we look at the issue ready, we tin can easily empathise that BookNumber: 3 and BookNumber: 4 are duplicate rows. Previously, it was explained in detail how to remove duplicates in SQL. Nosotros must delete them to keep the database consistent.
Once again, the following options arise:
- Delete where volume number (BookNumber) is greater than 2.
- Delete where BookNumber is 3 and four.
Permit united states of america cull the first selection. However, remember that it is just valid if in that location are no rows after the indistinguishable rows we are enlightened of.
Execute the following script:
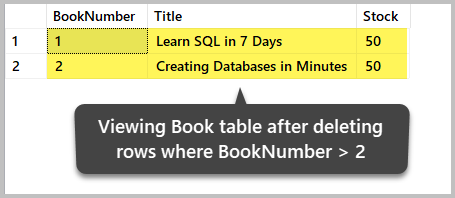
-- Delete all the data (rows) from the table Book where BookNumber is greater than 2 DELETE FROM dbo.Volume WHERE BookNumber>two View the data afterward the deletion
Let's check the table after deleting the information:
-- View data (rows) from the tabular array (Book) SELECT b.BookNumber, b.Championship, b.Stock FROM dbo.Book b The output is:
Insert more Data into the Tabular array (more Stock)
To put more than information (row) related to the stock, we employ the below script:
-- Insert rows into table 'Book' INSERT INTO [dbo].[Book] ( -- Columns to insert data into [BookNumber], [Title], [Stock] ) VALUES ( -- First row: values for the columns in the list above 3, 'Basic Data Structures', lx ), ( -- Second row: values for the columns in the listing higher up iv, 'Avant-garde Data Structures', 0 ) Become View data before deletion
Have a look at the table:
-- View data (rows) from the table (Book) SELECT b.BookNumber, b.Title, b.Stock FROM dbo.Book b The output is:
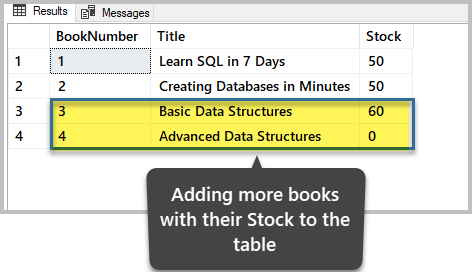
Delete the Data based on a Different Status
Presume that we demand to remove out of stock books to keep more accurate data in the database. To do this, we should expect for those rows with the Stock is 0.
Nosotros can apply the DELETE argument with the condition based on the Stock column value 0:
-- Delete all the out of stock (Where Stock is 0) books (rows) from the table Volume DELETE FROM dbo.Book WHERE Stock=0 View the data afterward the deletion
-- View data (rows) from the table (Book) SELECT b.BookNumber, b.Title, b.Stock FROM dbo.Volume b 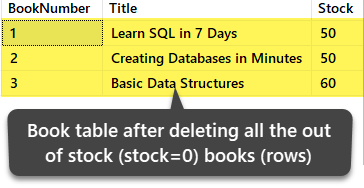
Insert More Data into Tabular array (More Titles and Stock)
We are adding two more than rows into the table:
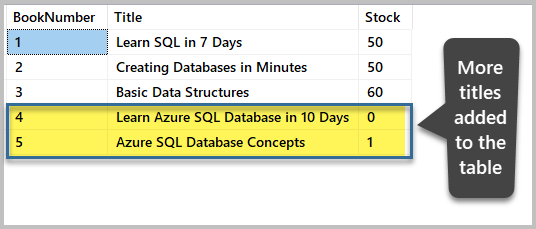
-- Insert rows into table 'Book' INSERT INTO [dbo].[Book] ( -- Columns to insert data into [BookNumber], [Title], [Stock] ) VALUES ( -- First row: values for the columns in the listing higher up iv, 'Acquire Azure SQL Database in x Days', 0 ), ( -- Second row: values for the columns in the list above 5, 'Azure SQL Database Concepts', i ) Become View the data before deletion
Check the rows earlier deleting annihilation further, based on the requirement:
-- View information (rows) from the table (Volume) SELECT b.BookNumber, b.Championship, b.Stock FROM dbo.Book b The table output is:
Delete the Information Based on 2 Conditions
This time, we need to delete all books (rows) where titles contain the word SQL and they are out of stock (their stock value is 0).
In other words, we delete all the SQL-related out of stock books.
In this case, we must specify more one condition with the DELETE statement. We take to ensure we are only deleting the out of stock books and merely those books having the word SQL in their title.
View the following script:
-- Delete all the out of stock (Where Stock is 0) SQL related (Title contains SQL) books (rows) from the table Book DELETE FROM dbo.Book WHERE Championship LIKE '%SQL%' and Stock=0 View the information after the deletion
Nosotros view the data for the final time:
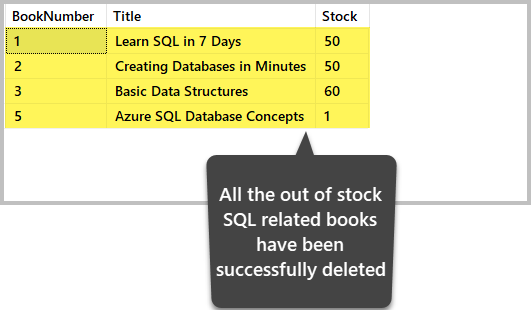
Important Tip: Before you delete the data, run the SELECT argument based on the same condition you are going to use for deletion. This way, you lot ensure that your deleting activities will use to the correct information.
For instance, run the SELECT query first to ensure that you are only getting those rows that are meant for deletion:
SELECT * FROM dbo.Volume WHERE Title LIKE '%SQL%' and Stock=0 Once you lot are confident, you tin turn your SELECT into the DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM dbo.Book WHERE Title LIKE '%SQL%' and Stock=0 Congratulations!
Yous have successfully mastered the chore of removing (deleting) ane or more rows from a table co-ordinate to the requirements.
Stay in touch for advanced deletion scenarios and other professional tips regarding the DELETE statement usage.
Things to Exercise
Now that you can remove rows from a tabular array successfully, you can train and improve your skills further:
- Endeavor to remove rows where there is only one item in the stock.
- Delete all the books where the championship contains the word Construction.
- Delete all the books (rows) except for book number (BookNumber) i.
Notice more advanced scenarios about the SQL DELETE argument.
(Visited 1,828 times, 20 visits today)
Tags: sql delete, sql server, t-sql, t-sql statements Last modified: September 17, 2021
radcliffe-brownbusind.blogspot.com
Source: https://codingsight.com/sql-server-delete-removing-one-or-more-rows-from-table/
0 Response to "what command would you use to delete the tasks table from the bits database?"
Post a Comment